SCCEI Spring Seminar Series
Wednesday, May 25, 2022 11:00 am -12:15 pm Pacific Time
Philippines Room, C330, 3rd Floor, Encina Hall Central, 616 Jane Stanford Way | Zoom Meeting
Economic Inequality and Social and Demographic Outcomes in China
In this talk, Professor Yu Xie will first document a sharp rise in economic inequality in contemporary China. He then will present results from his research program on the impact of rising economic inequality on a variety of social and demographic outcomes in China: intergenerational mobility, marriage age, marriage partner choice, fertility, and mortality.
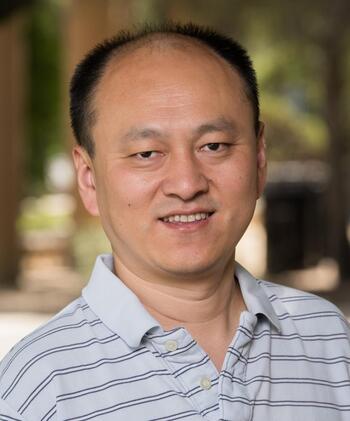
About the Speaker
Yu Xie is Bert G. Kerstetter ’66 University Professor of Sociology and has a faculty appointment at the Princeton Institute of International and Regional Studies, Princeton University. He is also a Visiting Chair Professor of the Center for Social Research, Peking University. His main areas of interest are social stratification, demography, statistical methods, Chinese studies, and sociology of science.
Xie's recently published works include: Marriage and Cohabitation (University of Chicago Press 2007) with Arland Thornton and William Axinn, Statistical Methods for Categorical Data Analysis with Daniel Powers (Emerald 2008, second edition), and Is American Science in Decline? (Harvard University Press, 2012) with Alexandra Killewald. Xie joined Princeton University in 2015, after 26 years at the University of Michigan, most recently as the Otis Dudley Duncan Distinguished University Professor of Sociology, Statistics and Public Policy and a research professor in the Population Studies Center at Michigan's Institute for Social Research. He is also a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, Academia Sinica and the National Academy of Sciences.
Seminar Series Moderators
Scott Rozelle is the Helen F. Farnsworth Senior Fellow and the co-director of Stanford Center on China's Economy and Institutions in the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies and Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research at Stanford University. For the past 30 years, he has worked on the economics of poverty reduction. Currently, his work on poverty has its full focus on human capital, including issues of rural health, nutrition and education. For the past 20 year, Rozelle has been the chair of the International Advisory Board of the Center for Chinese Agricultural Policy, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Most recently, Rozelle's research focuses on the economics of poverty and inequality, with an emphasis on rural education, health and nutrition in China. In recognition of this work, Dr. Rozelle has received numerous honors and awards. Among them, he became a Yangtse Scholar (Changjiang Xuezhe) in Renmin University of China in 2008. In 2008 he also was awarded the Friendship Award by Premiere Wen Jiabao, the highest honor that can be bestowed on a foreigner.
Hongbin Li is the Co-director of Stanford Center on China's Economy and Institutions, and a Senior Fellow of Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research (SIEPR) and the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies (FSI). Hongbin obtained his Ph.D. in economics from Stanford University in 2001 and joined the economics department of the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), where he became full professor in 2007. He was also one of the two founding directors of the Institute of Economics and Finance at the CUHK. He taught at Tsinghua University in Beijing 2007-2016 and was C.V. Starr Chair Professor of Economics in the School of Economics and Management. He founded the Chinese College Student Survey (CCSS) in 2009 and the China Employer-Employee Survey (CEES) in 2014.
Hongbin’s research has been focused on the transition and development of the Chinese economy, and the evidence-based research results have been both widely covered by media outlets and well read by policy makers around the world. He is currently the co-editor of the Journal of Comparative Economics.
A NOTE ON LOCATION
This seminar is a hybrid event. Please join us in person in the Philippines Room, C330, located within Encina Hall Central on the 3rd floor, or join remotely via Zoom.
Register once to receive the Zoom meeting link that will be used for all lectures in this series.

 FSI scholars approach their research on the environment from regulatory, economic and societal angles. The Center on Food Security and the Environment weighs the connection between climate change and agriculture; the impact of biofuel expansion on land and food supply; how to increase crop yields without expanding agricultural lands; and the trends in aquaculture. FSE’s research spans the globe – from the potential of smallholder irrigation to reduce hunger and improve development in sub-Saharan Africa to the devastation of drought on Iowa farms.
FSI scholars approach their research on the environment from regulatory, economic and societal angles. The Center on Food Security and the Environment weighs the connection between climate change and agriculture; the impact of biofuel expansion on land and food supply; how to increase crop yields without expanding agricultural lands; and the trends in aquaculture. FSE’s research spans the globe – from the potential of smallholder irrigation to reduce hunger and improve development in sub-Saharan Africa to the devastation of drought on Iowa farms.